Plot Multiple Vector and Raster Layers
Last updated on 2024-08-19 | Edit this page
Estimated time: 60 minutes
Overview
Questions
- How can I create map compositions with custom legends using ggplot?
- How can I plot raster and vector data together?
Objectives
- Plot multiple vector layers in the same plot.
- Apply custom symbols to spatial objects in a plot.
- Create a multi-layered plot with raster and vector data.
This episode builds upon previous episodes that work with vector layers in R and explore how to plot multiple vector layers. It also covers how to plot raster and vector data together on the same plot.
Load the Data
To work with vector data in R, we can use the sf
package. To work with raster data in R, we can use the
terra package. Make sure that you have these packages
loaded.
We will continue to work with the three ESRI shapefile
that we loaded in the Open and
Plot Vector Layers in R episode and the raster file we used in
previous episodes.
R
library(terra)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(sf)
R
# Load the data
aoi_boundary_HARV <- st_read("data/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/HarClip_UTMZ18.shp")
# If you are getting an error, check your file path:
# You might need change your file path to:
# "data/2009586/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/HarClip_UTMZ18.shp"
lines_HARV <- st_read("data/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/HARV_roads.shp")
# If you are getting an error, check your file path:
# You might need change your file path to:
# "data/2009586/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/HARV_roads.shp"
point_HARV <- st_read("data/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/HARVtower_UTM18N.shp")
# If you are getting an error, check your file path:
# You might need change your file path to:
# "data/2009586/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/HARVtower_UTM18N.shp"
CHM_HARV <- rast("data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/CHM/HARV_chmCrop.tif")
# If you are getting an error, check your file path:
# You might need change your file path to:
# "data/2009586/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/CHM/HARV_chmCrop.tif"
# Load the color palette from earlier lessons
road_colors <- c("blue", "green", "navy", "purple")
Plotting Multiple Vector Layers
In the previous episode, we learned how to plot information from a single vector layer and do some plot customization including adding a custom legend. However, what if we want to create a more complex plot with many vector layers and unique symbols that need to be represented clearly in a legend?
Now, let’s create a plot that combines our tower location
(point_HARV), site boundary
(aoi_boundary_HARV) and roads (lines_HARV)
spatial objects. We will need to build a custom legend as well.
To begin, we will create a plot with the site boundary as the first
layer. Then layer the tower location and road data on top using
+.
R
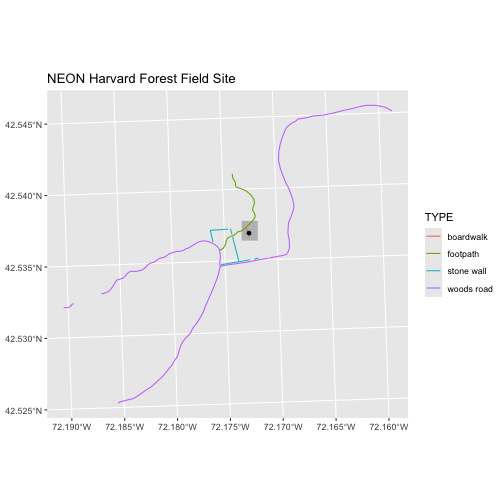
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = aoi_boundary_HARV, fill = "grey", color = "grey") +
geom_sf(data = lines_HARV, mapping = aes(color = TYPE)) +
geom_sf(data = point_HARV) +
labs(title = "NEON Harvard Forest Field Site") +
coord_sf()
Next, let’s build a custom legend using the symbology (the colors and symbols) that we used to create the plot above.
R
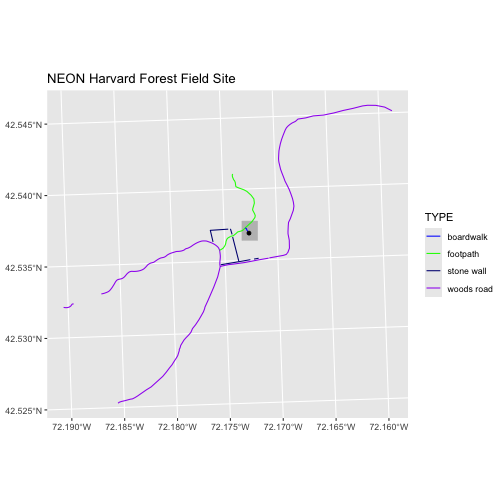
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = aoi_boundary_HARV, fill = "grey", color = "grey") +
geom_sf(data = lines_HARV, mapping = aes(color = TYPE)) +
geom_sf(data = point_HARV) +
scale_color_manual(values = road_colors) +
labs(title = "NEON Harvard Forest Field Site") +
coord_sf()
What if we wanted to have a legend for the tower location (the
point)? We can trick R into adding the legend for us, by specifying an
aesthetic and value to plot within the mapping = aes()
function for that layer. We’ve already used the color aesthetic in the
plot for the road colors, so we’ll have to use another aesthetic type
for getting the tower location to show up. In this example, let’s use
the fill aesthetic (note that there are also scales we can apply to the
point shape and alpha [transparency]).
We can do that by changing the line of code that plots the point:
geom_sf(data = point_HARV, aes(fill = "Tower location"))
This tells the plot that we want to color the “fill” of the point to be dictated by the “Tower location” label. We can pair this with a custom fill palette so that it’s plotted the way we want. For example:
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Tower location" = "black"))
This tells the plot that anything filled with the “Tower location” tag will actually be colored black.
R
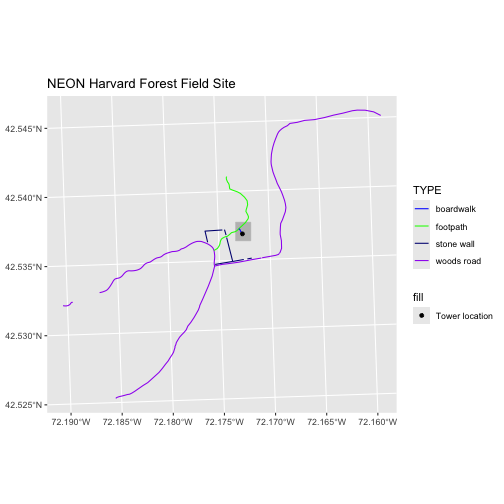
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = aoi_boundary_HARV, fill = "grey", color = "grey") +
geom_sf(data = lines_HARV, mapping = aes(color = TYPE)) +
geom_sf(data = point_HARV, mapping = aes(fill = "Tower location")) +
scale_color_manual(values = road_colors) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Tower location" = "black")) +
labs(title = "NEON Harvard Forest Field Site") +
coord_sf()
Now lets adjust the legend titles by passing a name to
the respective color and fill palettes. We can
do this within the color_scale_manual() and
color_fill_manual() functions, or within the
labs() function. If we don’t want a title for either of
those values, we can assign the name to NULL.
R
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = aoi_boundary_HARV, fill = "grey", color = "grey") +
geom_sf(data = lines_HARV, mapping = aes(color = TYPE)) +
geom_sf(data = point_HARV, mapping = aes(fill = "Tower location")) +
scale_color_manual(values = road_colors) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Tower location" = "black")) +
labs(title = "NEON Harvard Forest Field Site",
color = "Line Type",
fill = NULL) +
coord_sf()
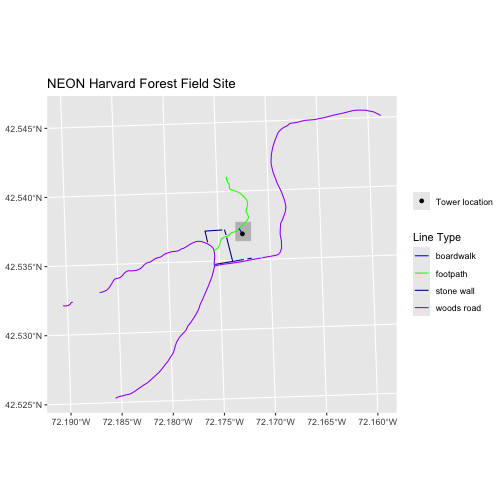
Finally, it might be better if the points were symbolized as a
symbol. We can customize this using shape parameters in our
call to geom_sf: 16 is a point symbol, 15 is a box.
R
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = aoi_boundary_HARV, fill = "grey", color = "grey") +
geom_sf(data = lines_HARV, mapping = aes(color = TYPE)) +
geom_sf(data = point_HARV, mapping = aes(fill = "Tower location"), shape = 15) +
scale_color_manual(values = road_colors) +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Tower location" = "black")) +
labs(title = "NEON Harvard Forest Field Site",
color = "Line Type",
fill = NULL) +
coord_sf()
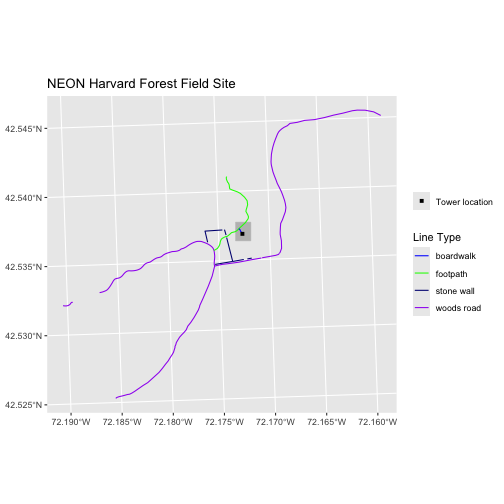
Challenge 1: Plot Polygon by Attribute
Using the
NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/PlotLocations_HARV.shpESRIshapefile, create a map of study plot locations, with each point colored by the soil type (soilTypeOr). How many different soil types are there at this particular field site? Overlay this layer on top of thelines_HARVlayer (the roads). Create a custom legend that applies line symbols to lines and point symbols to the points.Modify the plot above. Tell R to plot each point, using a different symbol of
shapevalue.
First we need to read in the data and see how many unique soils are
represented in the soilTypeOr attribute.
R
plot_locations <-
st_read("data/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/PlotLocations_HARV.shp")
OUTPUT
Reading layer `PlotLocations_HARV' from data source
`/Users/echelleburns/Documents/2024-07-01-ucsb-intro-geospatial/site/built/data/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/PlotLocations_HARV.shp'
using driver `ESRI Shapefile'
Simple feature collection with 21 features and 25 fields
Geometry type: POINT
Dimension: XY
Bounding box: xmin: 731405.3 ymin: 4712845 xmax: 732275.3 ymax: 4713846
Projected CRS: WGS 84 / UTM zone 18NR
# If you are getting an error, check your file path:
# You might need change your file path to:
# "data/2009586/NEON-DS-Site-Layout-Files/HARV/PlotLocations_HARV.shp"
unique(plot_locations$soilTypeOr)
OUTPUT
[1] "Inceptisols" "Histosols" Next we can create a new color palette with one color for each soil type.
R
blue_orange <- c("cornflowerblue", "darkorange")
Finally, we will create our plot.
R
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = lines_HARV, mapping = aes(color = TYPE)) +
geom_sf(data = plot_locations, mapping = aes(fill = soilTypeOr),
shape = 21) +
scale_color_manual(values = road_colors) +
scale_fill_manual(values = blue_orange) +
labs(title = "NEON Harvard Forest Field Site",
color = "Line Type",
fill = "Soil Type") +
coord_sf()
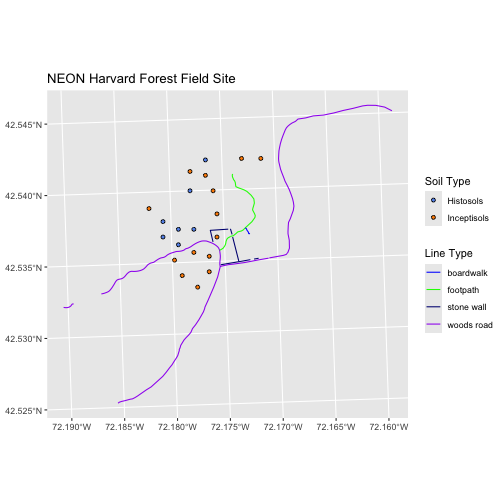
If we want each soil to be shown with a different symbol, we can give
multiple values to the scale_shape_manual() argument.
This get’s a little tricky though, because now we have a legend for the fill color and a legend for the shape for the soil type from the plot locations. We can override the aesthetics of the legends so that we only display one of the legends for the plot soil type - a legend that includes the right shape and the right colors. We do that by removing one of the legends from the plot and altering the legend we want to keep.
Let’s change the scale_shape_manual() to include the
appropriate fill colors for the points. To do this, we will use
guide = guide_legend() within the
scale_shape_manual() function. We override the aesthetics
by using override.aes and providing it with a list of
things to override.
Putting it all together results in a line of code that looks like
this:
scale_shape_manual(values = c(21, 22), guide = guide_legend(override.aes = list(fill = blue_orange)))
Here, we’re specifying that we want to keep the legend for the
shapes, but we want the legend (the guide) to look different than the
default. We want to override the default fill values (which is black) to
the colors in the blue_orange vector. This will make the
legend match the actual points on the plot.
It’s a lot to take in, we know, but it might come in handy for our own research!
R
ggplot() +
geom_sf(data = lines_HARV, mapping = aes(color = TYPE)) +
geom_sf(data = plot_locations, mapping = aes(fill = soilTypeOr, shape = soilTypeOr)) +
scale_color_manual(values = road_colors) +
scale_fill_manual(values = blue_orange, guide = "none") +
scale_shape_manual(values = c(21, 22),
guide = guide_legend(override.aes = list(fill = blue_orange))) +
labs(title = "NEON Harvard Forest Field Site",
color = "Line Type",
shape = "Soil Type") +
coord_sf()
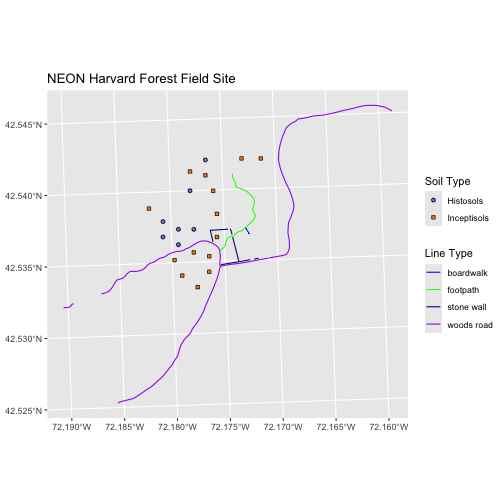
Plotting Raster & Vector Data Together
You can plot vector data layered on top of raster data using the
ggplot2 package or the tmap package.
We’ll first go into how to do this using ggplot, and
then we’ll create a similar plot using tmap.
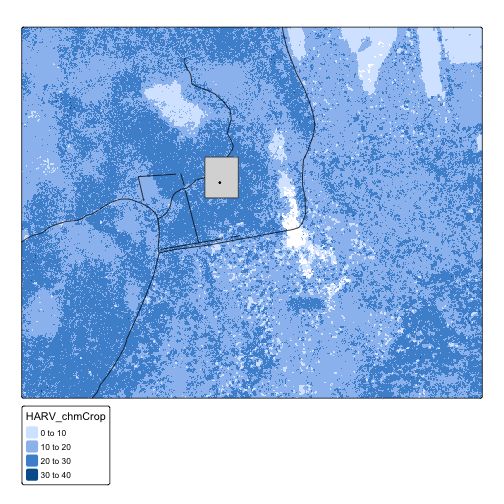
Together, let’s create a plot that uses the NEON AOI Canopy Height
Model
data/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/CHM/HARV_chmCrop.tif
(or
data/2009586/NEON-DS-Airborne-Remote-Sensing/HARV/CHM/HARV_chmCrop.tif
depending on your set up) as a base layer. On top of the CHM, we will
add the study site AOI, roads, and the tower location.
Remember for ggplot to be able to plot raster data, we
first need to convert it to a data frame.
R
CHM_HARV_df <- as.data.frame(CHM_HARV, xy = TRUE)
Now we can add it to the plot as a geom_raster()
object:
R
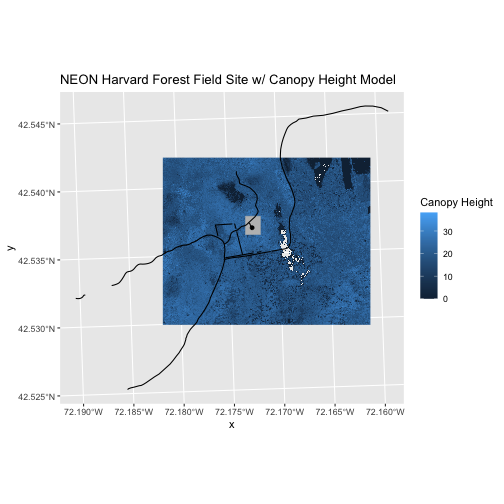
ggplot() +
geom_raster(data = CHM_HARV_df,
mapping = aes(x = x, y = y, fill = HARV_chmCrop)) +
geom_sf(data = aoi_boundary_HARV, fill = "grey", color = "grey") +
geom_sf(data = lines_HARV) +
geom_sf(data = point_HARV) +
labs(title = "NEON Harvard Forest Field Site w/ Canopy Height Model",
fill = "Canopy Height") +
coord_sf()
Now we can make a similar plot using tmap.
If you haven’t downloaded the tmap package yet, you can
do so by going to the Packages tab in your R console and installing a
new package, or you can type the following code into your R console:
install.packages("tmap")
Once downloaded, remember to load tmap into your
environment using:
R
library(tmap)
The syntax for tmap is to first specify a layer to plot
and then to specify the kind of layer it is. For example, if you wanted
to plot a raster first, and then a vector layer on top of it, you would
write something like this:
R
tm_shape(raster_object) + # first we specify the object to plot first
tm_raster() + # then we specify the kind of object it is
tm_shape(vector_object) + # then we specify the object to plot next
tm_sf() # then we specify the kind of object it is
You can specify things like color and shape within the
tm_sf() function as col = "black" or
shape = 8 for example.
R
# Create the plot
tm_shape(CHM_HARV) +
tm_raster() +
tm_shape(lines_HARV) +
tm_sf() +
tm_shape(aoi_boundary_HARV) +
tm_sf(col = "grey20") +
tm_shape(point_HARV) +
tm_sf(col = "black")
OUTPUT
SpatRaster object downsampled to 898 by 1115 cells.